Non-vegetarian food has long been an integral component of many diets; however, in recent times, there has been an emerging trend toward individuals adopting vegetarian or vegan lifestyles. Although there may be various motivations behind this move, we must understand its potential impacts on one’s health when giving up non-vegetarian foods completely from their diets and how doing so could impact overall well-being. This post intends to explore these effects by eliminating non-vegetarian items from our daily meals and how that might impact overall well-being.

Nutritional Considerations
Food sources that contain meat, poultry, and seafood are known for their high protein content. When transitioning to vegetarianism, it’s essential to find alternative protein-rich options to maintain a balanced diet; legumes, tofu, and quinoa may serve as good replacements. Furthermore, plant-based protein sources should include iron, zinc, and vitamin B12 supplements or alternatives, as these will prevent deficiencies from developing.

Reducing consumption of non-vegetarian food requires careful planning to meet essential fatty acid requirements, like omega-3. Fish is the main source of these beneficial fats; alternative sources like flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts may help meet them nutritionally.
Impact on Energy Levels
Non-vegan food can provide an abundant source of energy due to its rich protein and fat content. When eliminating these sources, however, individuals may initially experience decreased energy levels while their bodies adjust. It is important to counteract this energy loss by including energy-rich whole-grain foods, nuts, and seeds in one’s diet as a supplement.
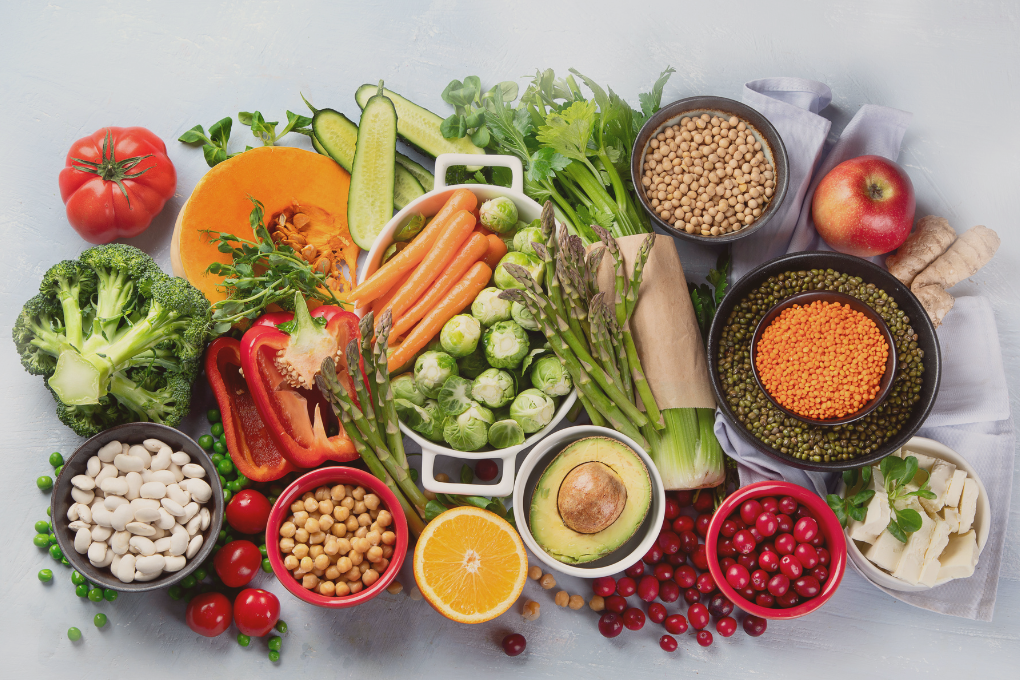

Digestive Health
Switching from non-vegetarian food sources can have a dramatic effect on digestive health. Non-vegetarian sources tend to contain plenty of fiber-rich non-veg sources that aid in digestion and prevent constipation, so those transitioning into vegetarian or vegan eating must ensure they consume adequate plant-based diets such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes in their diet to support an efficient digestive system.
Cholesterol and Heart Health
Non-vegetarian food, particularly red meat, has long been associated with higher levels of cholesterol and an increased risk of heart disease. Eliminating such products may result in reduced cholesterol levels and cardiovascular issues; however, to ensure optimal heart health, it is still necessary to eat a balanced diet including avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
Environmental Benefits
Beyond personal health considerations, transitioning away from non-vegetarian food can also have a beneficial effect on the environment. Meat production contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, and water pollution; thus, adopting a vegetarian or vegan lifestyle will contribute significantly toward reducing your carbon footprint and encouraging sustainable practices.

Though making the switch may have some negative effects on your health, navigating it with care can ensure a successful vegetarian or vegan lifestyle. By planning and ensuring adequate intake of essential nutrients, a mindful approach to this change in lifestyle is possible. For guidance or assistance regarding this decision, consult a healthcare provider or registered dietitian whose plan fits your nutritional requirements best. Remember, making informed choices regarding food can have positive results both for yourself and for our environment!






